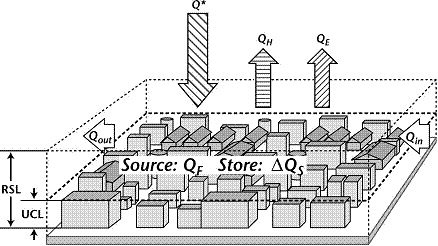
Fig. 1: Scheme of the urban energy balance ...
|
Hyper-Swiss-NetProject descriptionThe Hyper-Swiss-Net project aims at developing and supporting the scientific expertise and infrastructure in Switzerland for the exploitation of imaging spectrometry technology for different Earth observation applications. The development of imaging spectrometers, the availability of Earth observations in high spectral resolution from air- and spaceborne platforms as well as the facility of their processing has remarkably evolved over the last decade. This trend leads to a level of maturity, which makes imaging spectrometry accessible and useful for a larger research and user community. Against this background Hyper-Swiss-Net will develop a range of prototype application products drawing from the diverse expertise present in the project consortium and the respective user community. The development and implementation of the different products will be based on dedicated flight experiments with the airborne ESA imaging spectrometer APEX and will directly build on and link into the operational capabilities of the APEX processing and archiving facility (PAF). The scientific expertise gathered during the project will be further disseminated within the Swiss research community by integrating the developed capabilities into specific teaching modules. Project Modules
MCR contribution: The Urban ModuleThe architecture of urban areas reflects an extremely specific man-made structure introducing complex phenomena and influencing ecological, climatic and energetic conditions of the urban climate. Energy and radiation fluxes are the main drivers of urban climate, which significantly deviates from the climate of the rural surroundings. Together with standard techniques using helicopter-borne high-resolution thermal infrared camera, micrometeorological in situ measurements and numerical modelling, hyperspectral remote sensing data from the imaging spectrometer APEX open new opportunities for the assessment of the complete radiation and energy balance of a city (fig. 1.). The Urban Climatology Module in the frame of the HyperSwissNet project will further develop and refine existing urban specific methods in imaging spectrometry towards the assessment of specific fluxes in the radiation and energy balance of urban surfaces. Time table
Consortium and modulesRemote Sensing Laboratories, University of Zürich (Project coordination), Vegetation Dynamics Space Center EPFL, EPFL Lausanne, Geo-Biophysical Parameters Laboratory for Air Pollution and Environmental Technology, Empa, Atmospheric Trace Gases Remote Sensing Group, University of Bern, Snow and Climate Institute for Meteorology, Climatology and Remote Sensing, University of Basel, Urban Climatology Swiss Federal Research Institute WSL, Land Use Dynamics Project Websitehttps://hyperswissnet.wiki.geo.uzh.ch/Project Involved persons at MCR: |